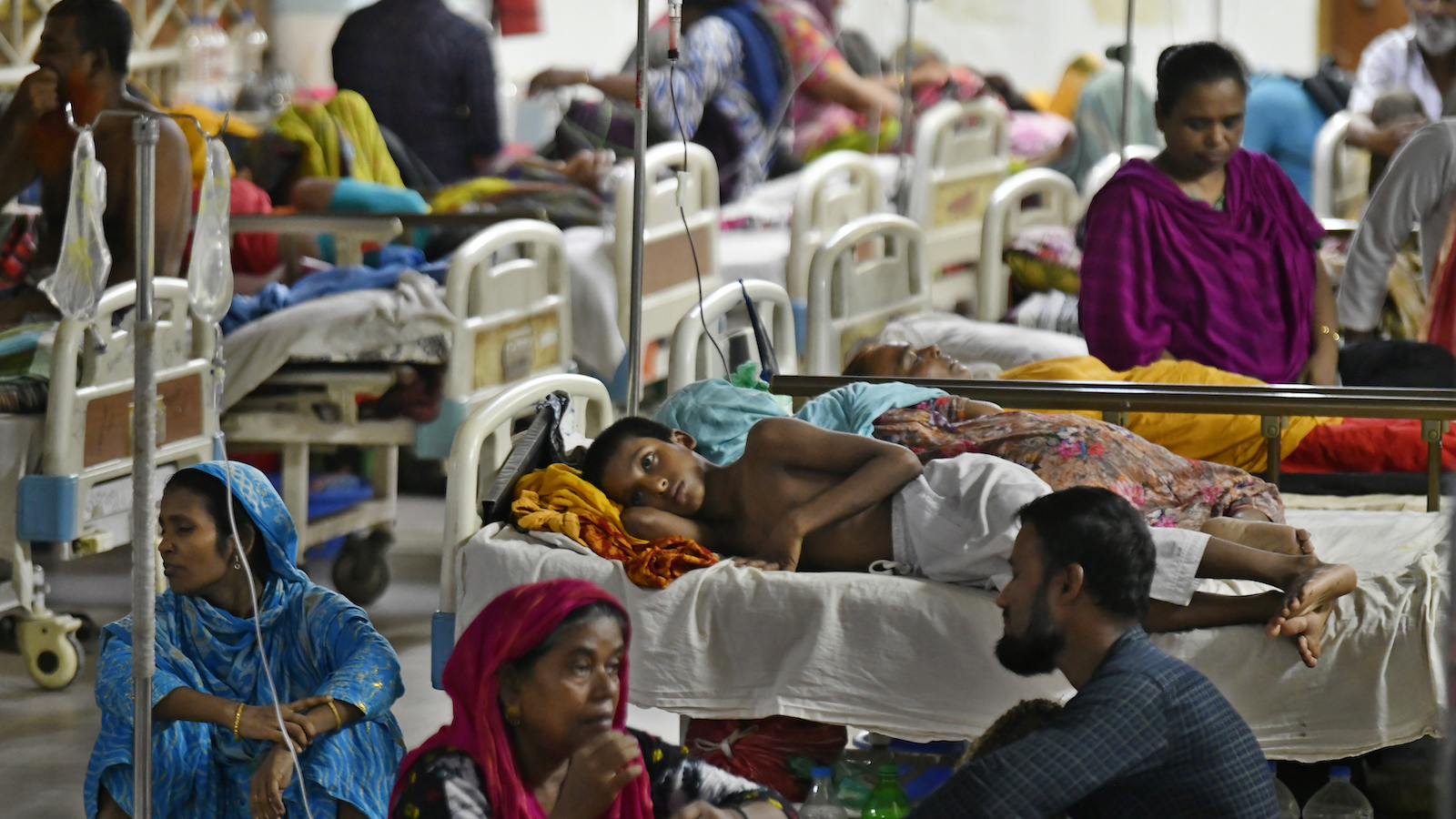
The monsoon season in Bangladesh sometimes runs from Could to September, with rainfall peaking in July and sputtering out in early October. This 12 months, nevertheless, there was extra rain than standard in October and even some showers in usually dry November. The additional rain, together with total hotter temperatures, contributed to a surge in circumstances of dengue fever, prolonging the nation’s largest and deadliest recorded outbreak of the mosquito-borne illness.
In accordance with knowledge from Bangladesh’s ministry of well being, 1,570 individuals have died and greater than 300,000 have been contaminated as of November 22. That’s 3 times the variety of infections recorded within the nation’s largest earlier outbreak, in 2019.
Dengue is a viral an infection transmitted to people by the chunk of contaminated Aedes aegypti or Aedes albopictus mosquitoes. The illness is typically referred to as “breakbone fever” for the aches and pains it may well produce. Whereas most circumstances of dengue are comparatively delicate, and signs will be handled, some sufferers develop dengue hemorrhagic fever, which will be deadly.
A World Well being Group official referred to as current dengue outbreaks a “canary within the coal mine of the local weather disaster.”
This 12 months’s dengue outbreaks haven’t been restricted to Bangladesh. Greater than 4.5 million circumstances and 4,000 deaths associated to dengue have been reported this 12 months, by way of the start of November, from 80 international locations. Greater than half of these circumstances had been in South America, with epidemics in Brazil, Peru, and Bolivia, however there have been additionally outbreaks in South and Southeast Asian international locations, together with Sri Lanka, Thailand, and Vietnam.
Dengue infections have been rising in tropical and subtropical areas for the previous twenty years: Circumstances reported to the World Well being Group (WHO) elevated from about half 1,000,000 in 2000 to five.2 million in 2019. Improved diagnostics and reporting clarify a lot of this leap, however a mix of inhabitants progress, rising urbanization and journey, and climatic modifications can be boosting Aedes mosquitoes, which drives up transmission in present hotspots and spreads it towards new areas at each larger latitudes and better altitudes. Lately, dengue has popped up in locations it had by no means been seen, together with Afghanistan, elements of Southern Europe, and, this 12 months, Chad.
In July, a senior WHO official flagged the position of rising temperatures and humidity ranges — along with this 12 months’s El Niño — calling the outbreaks a “canary within the coal mine of the local weather disaster.” About half the world’s inhabitants is already uncovered to dengue danger; a 2019 local weather modelling examine projected that underneath a average warming situation, a further 2 billion individuals can be liable to dengue publicity by 2080, in comparison with 2015.

Flooding after heavy rains in Dhaka, September 22, 2023.
Kazi Salahuddin Razu / NurPhoto through AP
Bangladesh’s disaster is thus “a wake-up name,” particularly for South Asia, mentioned Ayesha Mahmud, a well being demographer specializing in infectious illness on the College of California, Berkeley. “Understanding the affect of those drivers of dengue transmission might be essential for forecasting outbreaks sooner or later,” she added, “significantly within the context of predicted climatic modifications, similar to will increase in imply temperatures throughout the tropics and the intensification of the monsoon season.”
A warming and urbanizing world has been good for A. aegypti, the primary vector of the dengue virus. In accordance with the 2020 Lancet Countdown on Well being and Local weather Change, rising world temperatures between 1950 and 2018 elevated the local weather suitability for the transmission of the dengue virus by virtually 9 p.c for A. aegypti and 15 p.c for A. albopictus.
As temperatures proceed to rise, extra areas will develop into liveable for these mosquitoes. “Sooner or later, the belt of transmission goes to proceed increasing northwards and upwards,” mentioned Felipe Colón-González, a local weather and well being skilled on the Wellcome Belief, a worldwide charitable basis based mostly within the U.Ok. “There’s going to be extra months which are going to be appropriate for transmission, and since individuals are more likely to journey extra, there’s additionally going to be extra alternatives for shifting the mosquitoes and shifting the illness to totally different areas.”
In Bangladesh, dengue season may develop into longer as winter temperatures rise, resulting in outbreaks at any time of the 12 months.
The most important enhance in circumstances, mentioned Colón-González, is predicted in Southeast Asia — particularly elements of Malaysia, Indonesia, the Philippines, Vietnam, and a few areas of the Indian subcontinent — and in South America, significantly Brazil. Though inhabitants progress and urbanization will play greater roles in boosting danger, larger temperatures can enhance mosquito inhabitants density, their biting fee, and even their flying distances, research have proven.
In higher-warming eventualities, nevertheless, some areas in India, Bangladesh, and Thailand, amongst others, may develop into much less appropriate for A. aegypti, leading to a decline in circumstances within the second half of the century, in keeping with Colón-González’s local weather modeling. The optimum temperature vary for Aedes mosquitoes is regarded as 77 to 86 levels F (25 to 30 levels C).
Consultants additionally count on extra circumstances in elements of Africa, although projections for that area are troublesome to make as a result of lack of well being knowledge. Areas unfamiliar with dengue could also be onerous hit even when case numbers aren’t excessive, Colón-González warns, as individuals received’t have immunity from earlier publicity to the virus, and public well being techniques might not be sturdy sufficient to deal with dengue outbreaks. Even the place well being techniques are sturdy, similar to in Southern Europe or the US — which has recorded 1,874 circumstances in 2023, as of November 8 — medical doctors might not be capable to establish the illness. “Well being care suppliers ought to study to acknowledge this illness at an early stage,” says the Facilities for Illness Management and Prevention.

Aedes aegypti punctures human pores and skin, drawing blood.
Tacio Philip Sansonovski / Alamy Inventory Picture
Hotter temperatures may additionally increase the season for transmission. A 2021 examine exploring future danger for Bangladesh discovered that the dengue season may develop into longer as winter temperatures rise, resulting in “outbreaks occurring at any time of the 12 months.”
Modifications in rainfall can even form outbreak danger, as Bangladesh noticed this 12 months. Elevated rain means there may be extra stagnant water by which mosquitoes can breed, although deluges can even wash larvae away. And diminished rainfall can lead communities to retailer water, which creates alternatives for mosquitoes to breed. Researchers have additionally linked El Niño, a local weather phenomenon that brings heavy rain to some locations, with elevated incidence of dengue in Colombia and with outbreaks in Venezuela.
Dengue is commonly thought of an city illness as a result of A. aegypti thrives in cities, breeding even in tiny quantities of water and feeding on a big human inhabitants. Nonetheless, a current examine by Colón-González and others taking a look at transmission dynamics in Southeast Asia discovered that densely populated city areas could also be at decrease danger in comparison with surrounding or growing rural areas, maybe as a result of extremely developed cities are more likely to be wealthier and have higher infrastructure — from trash assortment to water entry — than newly urbanizing areas.
Being contaminated with one pressure of dengue doesn’t present immunity to others, and a second an infection may cause extra extreme illness.
Within the examine, larger GDP turned out to have a protecting impact towards dengue. Colón-González factors to the distinction in dengue incidence in cities on both aspect of the U.S.-Mexico border. “The variety of circumstances on the Mexican aspect is greater than 100 instances greater than on the U.S. aspect, even when they share the identical local weather,” he mentioned. “Folks [in the U.S.] have extra adaptive capability. They’ve entry to air con, [which] reduces humidity and temperature and the survival of mosquitoes.”
A post-pandemic enhance in building exercise can also be taking part in a job within the Bangladesh outbreaks, mentioned Kabirul Bashar, an entomologist and a member of the federal government anti-dengue committee, as a result of stagnant water can gather within the trenches and shafts of constructing websites. Fast and unplanned urbanization additionally implies that many areas don’t have a daily water provide, forcing individuals to retailer water, he famous. These areas might not have correct waste administration techniques both, resulting in massive portions of litter that gather water in shut proximity to houses. Within the capital of Dhaka, for example, analysis has discovered mosquitoes breeding in every thing from discarded tires and fridge trays to plastic drums and building waste.

A employee sprays insecticide in a crowded neighborhood in Dhaka to guard towards dengue fever, July 18, 2023.
Syed Mahamudur Rahman / NurPhoto through Getty Photographs
Latest years have additionally seen extra circumstances reported from past Bangladesh’s capital area. In 2023, circumstances have been reported from each district within the nation, with extra circumstances outdoors Dhaka than inside. The spatial enlargement can also assist clarify the upper loss of life toll, as beforehand unexposed populations get contaminated in areas with out satisfactory well being infrastructure.
The loss of life toll can also be defined by the presence of 4 totally different serotypes, or strains, of the dengue virus circulating within the area. Since 2019, the dominant pressure of dengue in Bangladesh has been DENV-3. However DENV-4 emerged in final 12 months’s outbreak, and the extremely virulent DENV-2 is reported to have dominated circumstances this 12 months, after a hiatus of 4 years. Being contaminated with one pressure doesn’t present immunity to others, and a second an infection may cause extra extreme illness, elevating the danger of loss of life. “When a brand new serotype is launched in a inhabitants that beforehand skilled epidemics of different serotypes, we’d see worse outcomes and extra extreme circumstances within the inhabitants,” mentioned Mahmud, of UC Berkeley.
The massive outbreaks lately might have their very own knock-on impact. “The evolution of the virus occurs sooner when there may be huge unfold and new serotypes [emerge], which in flip results in huge endemic outbreaks,” says Neelika Malavige, world head of the dengue program on the nonprofit Medication for Uncared for Illnesses initiative (DNDi).
Pesticides will be useful, however research have discovered that many mosquitoes in Dhaka have develop into immune to generally used pesticides.
Researchers are ramping up their efforts to seek out options. Historically, communities have targeted on vector management — decreasing the probabilities of a mosquito chunk by selling using window screens and mattress nets or attempting to eradicate mosquitoes solely with insecticide sprays. However as a result of Aedes is energetic throughout the day — in contrast to the malaria-carrying Anopheles — mattress nets are of restricted use, consultants observe. Spraying pesticides on breeding websites will be useful, mentioned Bashar, however research have discovered many mosquitoes in Dhaka have develop into immune to generally used pesticides. He believes higher waste disposal and common water provide are vital to decreasing mosquito breeding.
From a well being perspective, consultants say improved illness surveillance and public well being infrastructure might be wanted to detect circumstances early. Lately, researchers have been attempting out early warning techniques to forecast outbreaks utilizing fashions that combine components like rainfall and inhabitants density. Such a system has been tried with some success in Colombia; Colón-González’s crew is testing a warning system in Vietnam. And two vaccines lately grew to become out there, although they will’t be used with out confirming, through a lab check, whether or not a affected person has beforehand been contaminated with dengue.
For its half, DNDi is targeted on discovering remedies for the illness, which has been traditionally uncared for by the pharmaceutical sector. In August, it introduced a partnership with establishments in India, Thailand, Malaysia, and Brazil with the intention of discovering a protected and reasonably priced remedy throughout the subsequent 5 years. Noting that vector management has not been in a position to cease the unfold of dengue past endemic international locations, DNDi South Asia director Kavita Singh referred to as for extra funding to develop remedies and diagnostics. “Coordinated motion is required to combat dengue,” she mentioned.